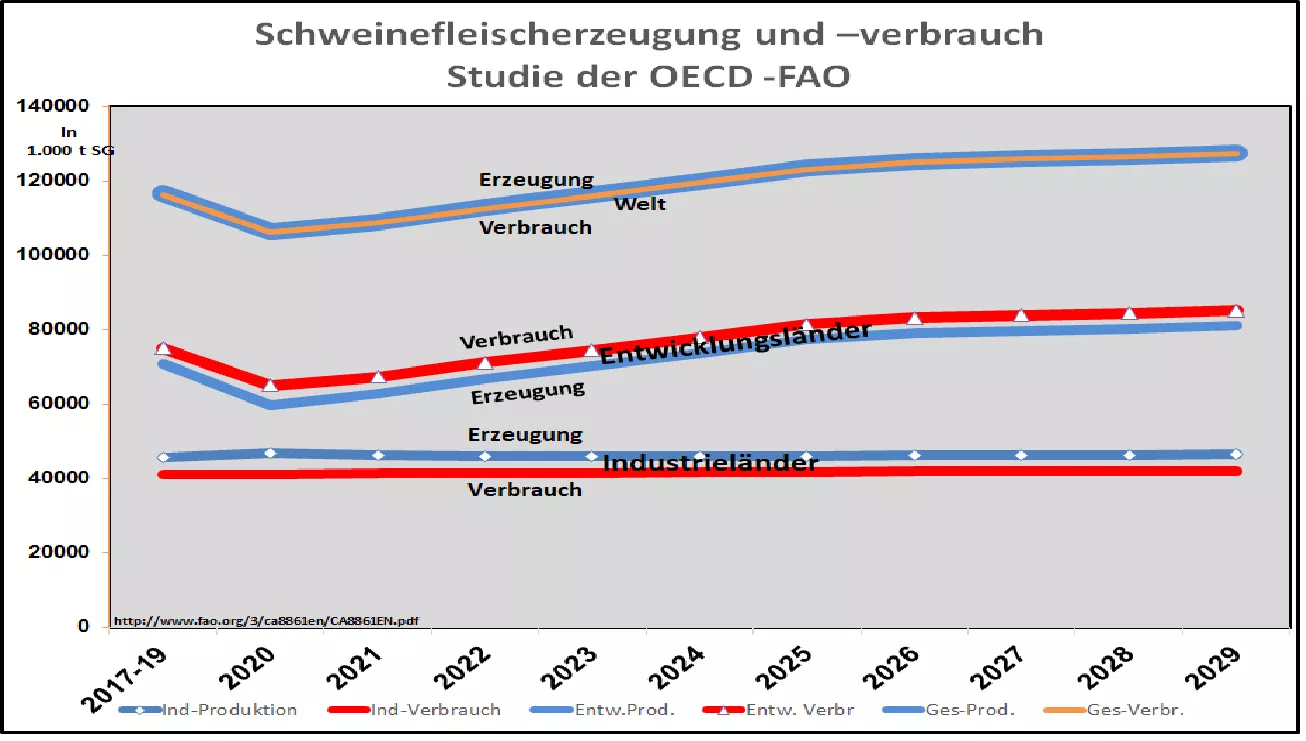
OECD FAO study: Pork production and -Consumption medium term measured by the average for the years 2017-19, the current pig meat market suffered a significant setback. The cause is the African swine fever (AFP), which has led to a halving of the herd in China , the world's largest production area. But the disease has also affected other Asian and Eastern European countries. Last but not least, the Covid19 pandemic should also be mentioned as a reinforcing factor. As a product with a very limited shelf life, reduced pork production also leads directly to reduced consumption . Production surpluses in one region are shipped to areas of need with the help of trade, so that production and consumption at world level are almost congruent. What's next for the next few years?A joint study by the OECD and FAO has addressed this question and has attempted to derive some fundamental developments. The main driving force for the development of the pork market comes from China . Pork is a staple in the world's largest population. A steadily increasing population and a remarkably high income growth lead to an exceptionally strong demand. The currently high Chinese pig prices above € 6 / kg are proof of this. Other Asian countries with ASP outbreaks also show similar, if not so clear, characteristics. The study assumes that the reconstruction of pig farming in 2026 will return to the level that existed in the pre-ASP period. By then, production and consumption should increase by 34% . In the aftermath, annual growth slows to just under 1% per year.Stagnant pork production and consumption are predicted in classic industrialized countries . On the production side, environmental problems are increasingly limiting further expansion. On the demand side, meat consumption has already reached saturation limits. Even further increases in income will no longer significantly increase average meat consumption. There is a trend towards poultry meat, which is better assessed in terms of price, health and the environment. Nevertheless, the study assumes that pork continues to be produced in the industrialized countries for export purposes . The excess demand existing in affluent developing countries leads to attractive prices. In addition, there are different appreciations for cuts of pork that favor an exchange. Last but not least, the production efficiency in the intensive locations is considerably higher than in most of the production regions at developing country level.According to the study, the global meat trade is expected to be 12% higher in 2029 than in the initial phase. Countries such as the EU, USA, Brazil and Canada are the main export countries. China is still at the forefront in the first few years on the import side , but is expected to introduce significantly falling quantities after 2026 due to increasing self-sufficiency. Other Asian importing countries will make up for part of the decline in Chinese imports.