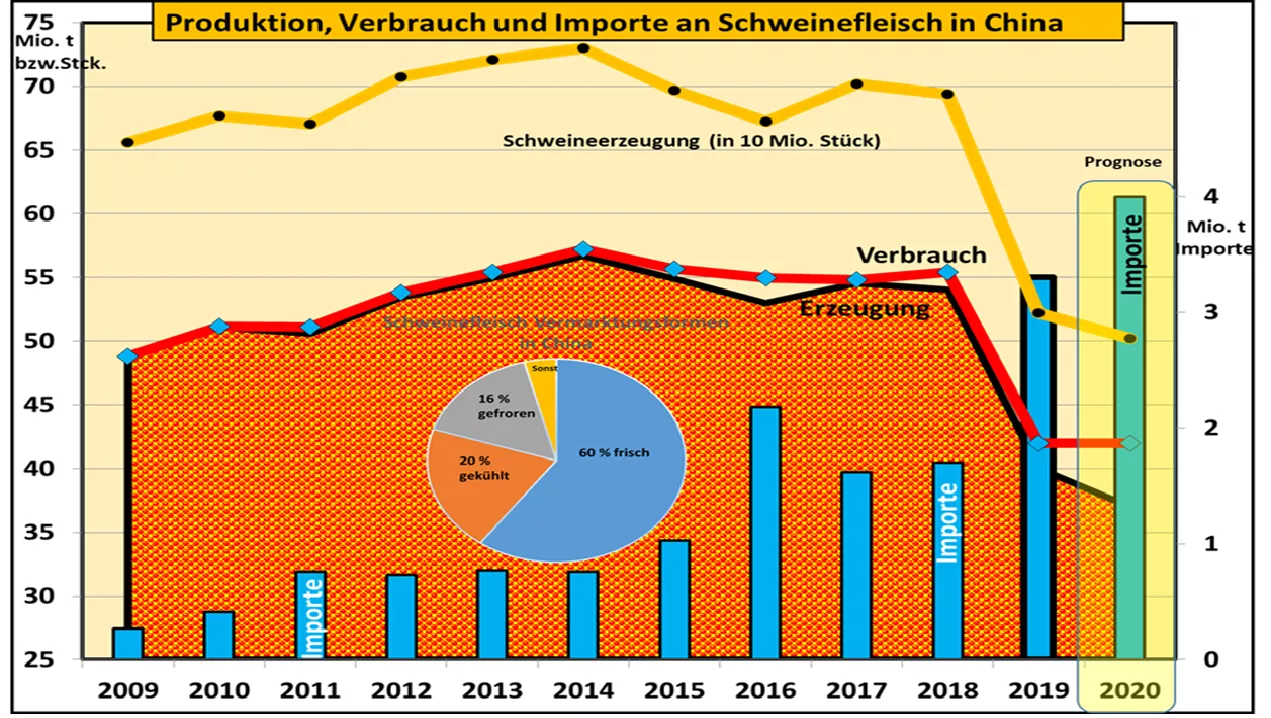
Is there a long-standing global demand for pork with long-term high prices? In the world's largest production region, China, with a 50% share of pigmeat production, fatal African swine fever (ASP) is rampant. Until the end of May 2019, according to official information, approx. Slaughtered 25% of sows and pigs year on year. According to estimates, approx. 30% of the formerly customary pork offer fail, a shortfall of approx. 16 million t. The progressive spread of ASP in Vietnam, Cambodia and other Southeast Asian countries is increasing the global supply problem by at least another 2.5 million tonnes. Huge dimension The Chinese deficit corresponds to the annual production of the USA and Brazil taken together. Throughout the EU, approx. 24 million t produced. Germany produces approx. 5.3 million tons per year. The entire world trade in pork so far comprises approx. 8.5 million t. World trade would have to triple in mathematical terms if China wanted to achieve full compensation through imports.But there is still enough meat in China from ongoing inventory cuts, frozen supplies and increasing imports. On the demand side, significantly less consumption is made, other types of meat are switched and more vegetable products are used again. Incidentally, during the summer season in China there is a seasonal weak demand. The stable Chinese pork prices have stopped after a price jump of 2.30 € / kg to more than 2.65 € / kg in the spring months for 3 months. Consumption highlights are the autumn / winter months until the Chinese New Year in early February. The supply is missing But the thick end is yet to come. The reduction of sow stocks leads to missing piglets and fattening pigs in the following years. Shortages on this scale can not be compensated for the time being. China will be forced to partly abandon the traditionally high Chinese pork consumption. However, other types of meat are available only to a limited extent. In the case of poultry meat, there is the contagious problem with human dangerous poultry viruses.Loss of production If, in a first rough calculation, only 20% of the shortfall in pork imports is assumed, 3.3 million tonnes of additional international supplies would be necessary. This corresponds to an increase of the previous world trade by 40%. The EU, Canada, Brazil, the USA and, soon, maybe Russia, are considered as exporting countries. The USA produce approx. 12 million t and export 2.6 million t; however, the relationship between the US and China is not the best. The EU is already struggling to maintain its production of 24 million tonnes and 4 million exports. The production conditions in this country are rather worse than better. The exception is Spain with growth potential. Brazil generates 3.7 million tonnes and exports 0.85 million tonnes to date. Canada already exports 1.25 million tonnes of its 1.8 million tonnes of pork production. Russia has not yet run 0.1 million tons, but is on the go. Temporal dimension The temporal dimension is even more serious. Experts predict that China will need up to a decade to get the ASP under control.It is referred to Spain that took 40 years to eradicate the ASP. Also, the reference to Eastern Europe makes thoughtful. There the ASP can not be decisively pushed back since the outbreak in the year 2007 in 12 years. The only successful country is the small Czech Republic. First laboratory successes with drugs are still a long way from safe use in practice. The complex ASP virus with its 160 proteins has so much variable infection potential that a few active ingredients will not be sufficient for safe control. The problems of China In contrast to Eastern Europe with predominantly wild boars, the ASP virus in China is mainly found in pigs. The spread of the disease in China is reinforced by the following factors:
- An almost 50% backyard and small-scale holdings, which offer a nationwide high reinfection potential due to lack of hygiene and ignorance.
- Still widespread feeding of non-heated kitchen waste
- High proportion of live animal transports from cheap to high-priced subsidy regions over thousands of kilometers, because a closed cold chain is still in its infancy.
- Rd. 350 million migrant workers who unknowingly carry infected food and spread the virus
- For fear of state repression, the reluctance of those affected to take an active part in active disease control: high levels of underreporting, inadequate disposal.
Reconstruction in the Far East The courage to rebuild a Chinese pig population is low given the high risk of reinfection. This applies to both small and large attitudes. A return to old conditions is not foreseeable in the next few years. A huge structural break is imminent. An increasing population of China and rising incomes lead to a greater demand for higher refined food. Pork is traditionally the top priority in China.Conclusion: The global demand for meat with a focus on China will persist for years and can not be met in a short time by production increases even close to complete. Available quantities of meat are bought immediately, with the exception of the last batch. The market will be empty. Last but not least, there is growing concern about introduction in the still ASP-free production areas.